The Evolution of the Internet: Web1, Web2, and Web3

The internet has changed a lot since it was first created, and to understand what Web3 is, it's important to know how it evolved through Web1 and Web2.
Web1: The "Static Web"
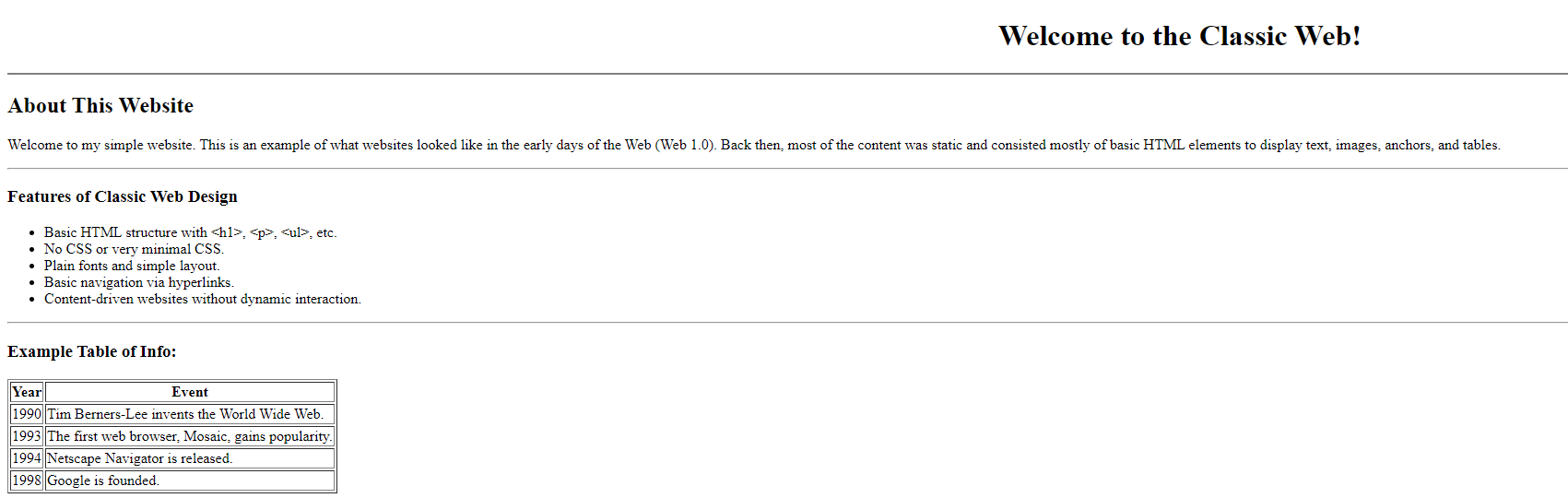
Web1 was the earliest version of the internet (1990s-2000s). It was mostly "read-only," meaning people could visit websites, but they couldn’t do much other than read information. There was no interaction, no sharing, and no social media.
Main features of Web1:
- Simple websites without much interaction.
- Users mostly read content but couldn’t create or share anything.
- No social media, blogs, or user-generated content.
Think of it as a giant online library — lots of information, but no interaction.
Web2: The "Social Web"
![]()
Web2 is what most of us use today. It started in the mid-2000s and brought interactive websites, allowing people to not only read but also create and share their own content. This is the era of social media, with platforms like Facebook, Instagram, and YouTube.
Main features of Web2:
- Users can create content (videos, blogs, photos).
- Websites are more interactive (you can like, comment, share).
- Big companies (like Google and Facebook) control and store your data.
While Web2 made the internet more fun, it also handed over most control to large tech companies, which raised concerns about privacy and data control.
Web3: The Decentralized Web

Web3 is the next phase of the internet. It aims to give control back to the users rather than big companies. Web3 is built on blockchain technology, which means that no single company owns your data; everything is decentralized.
Key features of Web3:
- Decentralization: Your data isn’t stored by a single company. Instead, it’s spread across many computers, giving you control.
- Blockchain: Think of this as a secure, digital ledger where data is recorded across multiple computers, making it almost impossible to change retroactively.
- Cryptocurrencies & Tokens: Web3 uses digital tokens like Bitcoin and Ethereum, which allow you to trade or buy things without needing a bank.
- Ownership Over Digital Assets: You truly own digital things like art or web domains using NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens), and only you can control or sell them.
In short, Web3 is about taking back ownership of your online data and assets.
What Makes Up Web3?
Here’s a quick look at the main components that make Web3 different:
-
Blockchain Technology: This is the foundation of Web3. Instead of a big company storing your data, it’s stored across many computers around the world, making it safer and more open.
-
Decentralized Apps (DApps): These are apps that don’t rely on one company to work. For example, there are DApps for trading money (without using banks) or even for social media, where you own your data.
-
Tokenized Domains & ENS (Ethereum Name Service): You can own a web domain as a digital asset (NFT). Instead of long, hard-to-remember blockchain addresses, you can have an easy name like "yourname.eth."
-
Decentralized Ownership and Voting (DAO): Some Web3 networks let users own tokens that give them voting rights on how things are run, making decisions more community-driven instead of controlled by one company.
In summary, Web3 is about giving the power back to the people by allowing them to control, own, and even govern their online data and assets using blockchain technology.

